
There is nothing particularly remarkable about the inventory turnover ratio, but the fixed asset turnover ratio is remarkable. Liquidity ratios measure a company’s ability to meet its short-term obligations. Key liquidity ratios include the current ratio, quick ratio, and cash ratio analysis formulas ratio. They are important because they help assess whether a company has sufficient assets to cover its short-term liabilities, indicating financial stability. Quick ratio The quick ratio (acid test) recognises that inventory often takes a long time to convert into cash.
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
Again, for liquidity purposes the shorter this period the better, as less cash is tied up in inventory. Also, long inventory holding periods can result in obsolete inventory. On the other hand, too little inventory https://www.bookstime.com/ can result in production stoppages and dissatisfied customers. Ratio analysis can be used to evaluate the performance of the company in terms of profitability, liquidity, efficiency and solvency.
- The balance sheet item should reflect the whole period as well; that’s why we average the beginning and ending balances.
- Ratio analysis is the quantitative interpretation of the company’s financial performance.
- When using this ratio to analyze a company, it can help to look at both the company growth phase and the industry as a whole.
- The management of a company can also use financial ratio analysis to determine the degree of efficiency in the management of assets and liabilities.
- The ones listed here are the most common ratios used in evaluating a business.
- This is because the income statement item pertains to a whole period’s activity.
- As you can see, it is possible to do a cursory financial ratio analysis of a business firm with only 13 financial ratios, even though ratio analysis has inherent limitations.
Financial Ratio Analysis: Definition, Types, Examples, and How to Use

Market prospect ratios help investors to predict how much they will earn from specific investments. The earnings can be in the form of higher stock value or future dividends. Investors can use current earnings and dividends to help determine the probable future stock price and the dividends they may expect to earn. Ratio analysis refers to the analysis of various pieces of financial information in the financial statements of a business.
- Book Value Per Share (BVPS) is a financial measure used in stock market analysis to determine the per-share value of a company based on its equity available to common shareholders.
- When a company generally boasts solid ratios in all areas, any sudden hint of weakness in one area may spark a significant stock sell-off.
- The capital turnover ratio measures the effectiveness with which a firm uses its financial resources.
- Essentially, it tells you how easily a company could pay its liabilities with cash.
- You can also try these financial ratios for estimating profitability.
- For example, a company with a 10% gross profit margin may be in good financial shape if other companies in the same sector have gross profit margins of 5%.
Average Collection Period
If there are problems with any of the other total assets, it will show up here, in the total asset turnover ratio. They are not using their plant and equipment efficiently to generate sales as, in both years, fixed asset turnover is very low. If your inventory turnover is rising, that means you are selling your products faster. If it is falling, you are in danger of holding obsolete inventory.

Interest Coverage Ratio
Also known as the working-capital ratio, the current ratio tells you how likely a company is able to meet its financial obligations for the next 12 months. You might check this ratio if you’re interested in whether a company has enough assets to pay off short-term liabilities. Liquidity ratios can give you an idea of how easily a company can pay its debts and other liabilities. That can be especially important when considering newer companies, which may face more significant cash flow challenges compared to established companies. A financial ratio is a means of expressing the relationship between two pieces of numerical data. When discussing ratios in a business or investment setting, you’re typically talking about information that’s included in a company’s financial statements.

- The resulting ratio can be interpreted in a way that is more insightful than looking at the items separately.
- Consider a business that made $1 billion in revenue last quarter.
- The ratios are drawn from a company’s past and present financial data.
- Profit before interest and tax (PBIT), can also be given as Operating profit.
- This fact means that the return on equity profitability ratio will be lower than if the firm was financed more with debt than with equity.
- Liquidity ratios give investors an idea of a company’s operational efficiency.
Payable days represent the average number of days a company takes to make the payment to its suppliers. The reason is that when we think about receivables, it directly comes from Sales made on a credit basis. However, the Cost of Goods sold is directly related to inventory and is carried on the balance sheet at cost.
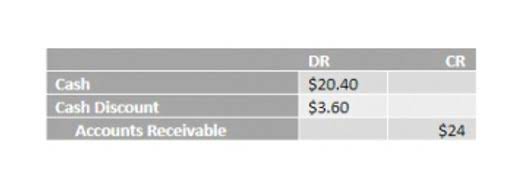
What is Accounts Payable Turnover?

